Acetabular Canal. Part 3
S.V. Arkhipov, Independent Researcher, Joensuu, Finland
Abstract
This article describes the space where the ligamentum capitis femoris (LCF) attaches and functions. See also Part 1 and Part 2.
The Significance of the Acetabular Canal
The
acetabular canal contains the main areas of attachment for the LCF (ligamentum capitis
femoris). Its distal end attaches to the femoral head, while the proximal end
connects to the fossa and notch of the acetabulum. The primary purpose of the
acetabular canal is to ensure the normal functioning of the LCF. Normally, the
LCF should not come into contact with the joint surfaces. Therefore, the length
of the LCF should not exceed the diameter of the acetabular fossa, i.e., the
diameter of the central section of the acetabular canal Its depth should be
less than the thickness of the LCF.
 |
Figure 1. Lateral wall of the acetabular canal and LCF; the bottom of the acetabulum is removed (from 1908GrayH). |
The
diameter and depth of the acetabular fossa, and thus the acetabular canal, are
critical dimensions for the LCF. A reduction in depth results in the bottom of
the acetabular fossa approaching the articular surface of the femoral head,
which has been observed by us and other authors in the older age group (1972ПодрушнякЕП; 2012АрхиповСВ). In this case, the LCF becomes compressed
between the lateral wall of the acetabular canal—the cartilage surface of the
femoral head—and the medial wall, the bottom of the acetabular fossa, covered
by synovial and adipose tissue. Figuratively speaking, even in a normal state,
the LCF is constantly caught "between Scylla and Charybdis."
Continuing with this analogy, it can be said that the compressed LCF within the
acetabular canal will inevitably be destroyed, much like the ships destroyed by
the clashing rocks of the Symplegades in Greek mythology. The gradual
compression of the LCF leads to its flattening and thinning due to abrasion, as
well as histological transformation. As the LCF becomes fragile, it tears under
what were previously normal stretching loads.
Visualization of the Acetabular Canal
Due
to the deep location of the hip joint, it is impossible to palpate the entrance
to the acetabular canal, let alone see it with the naked eye. The acetabular
canal only exists when the femoral head and the acetabulum are in articulation.
In ancient times, the contents of the acetabular canal were studied during
post-mortem dislocation of the femoral head. It was first observed during the
preparation of a deceased body for burial. The first post-mortem arthrotomy of
the hip joint with hip disarticulation is presumed to have occurred in Morocco
15,000-12,500 years ago (2016MariottiV_CondemiS). Remains of a human aged
8,000-4,500 years with signs of hip disarticulation were discovered in southern
China (2024YeZ_LiFJ). The acetabular canal was also examined during the
preparation of bodies for mummification. The oldest embalmed body discovered in
Chile is approximately 7,900±180 years old (1984AllisonMJ_LowensteinJM).
It
seems that the first physicians to observe the acetabular canal were Herophilus
of Chalcedon and Erasistratus of Ceos. These anatomists, in the 3rd-2nd century
BCE, conducted hundreds of dissections in Alexandria (1831CelsusAC). The
first to propose access to the acetabular canal by removing the anterior wall
of the acetabulum was P.N. Gerdy (1833). The first successful penetration into
the acetabular canal from the pelvic side was performed by W. Weber and E.
Weber, who drilled a hole in the bottom of the acetabular fossa (1836WeberW_WeberE). The contents of the acetabular canal were first observed from the
medial side by J. Struthers and G.M. Humphry. They made an opening in the bottom of the acetabular fossa (1858StruthersJ; 1858HumphryGM).
 |
| Figure 2. Lateral wall of the acetabular canal and LCF; the bottom of the acetabulum is removed (from 1904FickR). |
Today,
the study of the acetabular canal is inconceivable without the use of
instrumental methods. Its visualization is available radiologically, for
example, via plain radiography of the hip joint.
In
radiography, the transverse ligament in the outer segment of the peripheral
part of the acetabular canal is indistinguishable. As a result, this segment
appears larger in cross-section on the X-ray than in reality. In children, the
contents of the acetabular canal can be visualized using ultrasound.
Radiography
allows visualization of the medial and lateral walls of the acetabular canal. A
detailed view of its shape and dimensions can be obtained using computed
tomography (CT) of the hip joint.

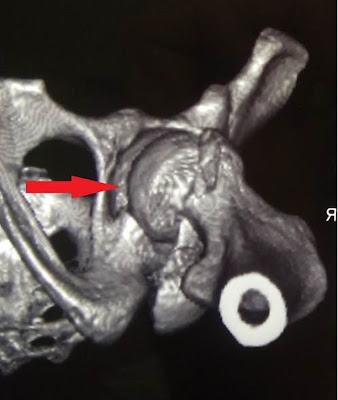
Three-dimensional
reconstruction of CT scans of the hip joint enables visualization of the
"entrance" to the acetabular canal, specifically the external opening
of the acetabular notch.

Viewed
from below during X-ray tomography, the "entrance" to the acetabular
canal has a pear-shaped form. It is wider at the back and narrower at the
front. In cases of hip joint trauma, the configuration of the external opening
leading to the acetabular canal may change.
In
some cases, CT of the hip joint reveals a shadow of the LCF in the acetabular
canal. More detailed visualization of the contents of the acetabular canal can
be achieved using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the hip joint.
MRI,
especially with contrast, allows differentiation of the contents of the
acetabular canal: LCF, adipose tissue accumulation, cartilage surfaces,
synovial fluid, synovial membrane folds, and the transverse ligament of the
acetabulum.
As age increases, the depth of the acetabular fossa decreases and may even disappear entirely (1972ПодрушнякЕП). We observed the absence of the acetabular canal in the fourth stage of osteoarthritis.
The
fossa and notch of the acetabulum usually disappear in protrusion coxarthrosis.
Additionally, the acetabular canal may become filled with fibrous tissue,
osteophytes, chondral bodies, and cartilage fragments. Newly formed bone and
scar tissue, a deformed acetabular fossa, free joint bodies, as well as
osteophytes from the deformed femoral head and the internal edges of the lunate
surface, lead to damage of the LCF during movement (see Pathology of the
Acetabular Canal). We believe this is one of the reasons for the disappearance
of the LCF.
References
Allison MJ, Focacci G, Arriaza B, Standen V, Rivera M, Lowenstein JM. Chinchorro, momias de preparación complicada: métodos de momificación. Chungara: Revista de Antropología Chilena. 1984;13:155-73.
Celsus AC. On medicine, in eight books, Latin and English. Translated from L. Targa's edition, the words of the text being arranged in the order of construction. To which are prefixed, a life of the author, tables of weights and measures, with explanatory notes, etc. designed to facilitate the progress of medical students. By Alex. Lee, A.M., Surg. In two volumes. London: E. Cox, MDCCCXXXI [1831].
Gerdy PN. Physiologie médicale, didactique et critique. T. 1. Paris: Librairie de Crochard, 1833.
Gray H. Anatomy, descriptive and surgical; 17th ed. Philadelphia, New York: Lea & Febiger, 1908.
Fick R. Handbuch der Anatomie und Mechanik der Gelenke: Erster Teil: Anatomie der Gelenke. Jena: G. Fischer, 1904.
Humphry GM. A Treatise on the Human Skeleton including the Joints. Cambridge: MacMillan and Company, 1858.
Mariotti V, Belcastro MG, Condemi S. From corpse to bones: funerary rituals of the Taforalt Iberomaurusian population. Bulletins et Memoires de la Societe d'Anthropologie de Paris. 2016;28(1-2)60-5.
Struthers J. Demonstration of the use of the round ligament of the hip joint. Edinburgh Med J. 1858;4(5)434-42.
Weber W, Weber E. Mechanik der menschlichen Gehwerkzeuge: eine anatomisch-physiologische Untersuchung. Gottingen: Dietrichsche Buchhandlung, 1836.
Ye Z, Wang M, Stock JT, Li FJ. Disarticulation, evisceration and excarnation: Neolithic mortuary practices at Dingsishan, southern China. Antiquity. 2024;98(399)616-35.
Архипов СВ. Роль связки головки бедренной кости в патогенезе коксартроза: дис. … канд. мед. наук. Москва, 2012.
Подрушняк ЕП. Возрастные изменения суставов человека. Киев: Здоров‘я, 1972.
Keywords
ligamentum capitis femoris, ligamentum teres, ligament of head of femur, acetabular canal, anatomy, attachment
NB! Fair practice / use: copied for the purposes of criticism, review, comment, research and private study in accordance with Copyright Laws of the US: 17 U.S.C. §107; Copyright Law of the EU: Dir. 2001/29/EC, art.5/3a,d; Copyright Law of the RU: ГК РФ ст.1274/1.1-2,7








Comments
Post a Comment