Fragments from the book Gray H. Anatomy, descriptive and surgical (1908; 17th ed.). The selected passages on the anatomy of the ligamentum capitis femoris (LCF) and illustrations.
Quote p. 220
The Cotyloid Cavity or Acetabulum. The cotyloid cavity, or acetabulum, is a deep, cup-shaped, hemispherical depression, directed downward, outward, and forward; formed internally by the os pubis, above by the ilium, behind and below by the ischium, a little less than two-fifths being formed by the ilium, a little more than two-fifths by the ischium, and the remaining fifth by the pubic bone. It is bounded by a prominent, uneven rim, which is thick and strong above, and serves for the attachment of the cotyloid ligament, which contracts its orifice and deepens the surface for articulation. It presents below a deep notch, the cotyloid notch (incisura acetabuli), which is continuous with a circular depression, the fossa of the acetabulum (fossa acetabuli), at the bottom of the cavity: this depression is perforated by numerous apertures, lodges a mass of fat, and its margins, as well as those of the notch, serve for the attachment of the ligamentum teres. In front, above and behind the fossa acetabuli, is a concave rim of bone (facies lunata). The cotyloid notch is converted, in the natural state, into a foramen by a dense ligamentous band which passes across it. Through this foramen the nutrient vessels and nerves enter the joint.
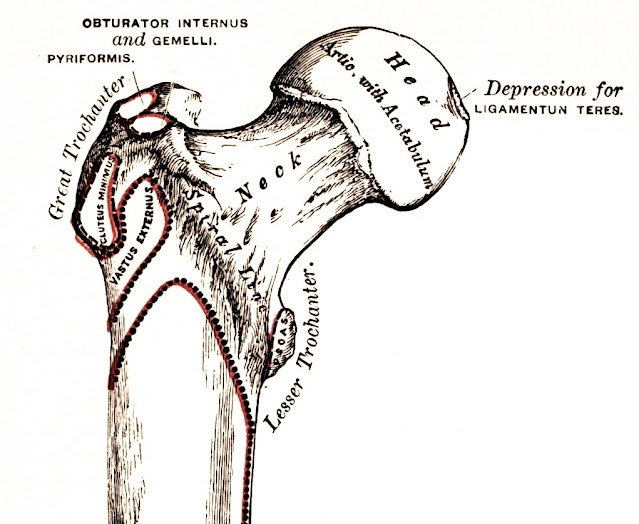 |
| Fig. 162. — Right Femur. Anterior Surface. [fragment] |
Quote p. 232
Fractures of the femur are divided, like those of the other long bones, into fractures of the upper end; of the shaft; and of the lower end. The fractures of the upper end may be classified into (1) fracture of the neck; (2) fracture at the junction of the neck with the great trochanter; (3) fracture of the great trochanter; and (4) separation of the epiphysis, either of the head or of the great trochanter. The first of these, fracture of the neck, is usually termed intracapsular fracture, but this is scarcely a correct designation, as owing to the attachment of the capsular ligament, the fracture may be partly within and partly without the capsule, when the fracture occurs at the lower part of the neck. It generally occurs in old people, principally women, and usually from a very slight degree of indirect violence. Probably the main cause of the fracture taking place in old people is in consequence of the degenerative changes which the bone has undergone. Merkel believes that it is mainly due to the absorption of the calcar femorale. These fractures are occasionally impacted. As a rule they unite by fibrous tissue, and frequently no union takes place, and the surfaces of the fracture become smooth and eburnated. The lack of reparative power in intracapsular fracture is due to lack of apposition of the fragments and diminution in the amount of blood sent to the smaller fragment. The head of the bone receives blood from the neck through the reflected portions of the capsule and through the Ligamentum teres. A fracture cuts off the supply by the neck and by the reflected portions of the capsule.
 |
| Fig. 234. Right hip-joint, from in front. (Spalteholz.) |
Quote p. 224
Its surface is smooth, coated with cartilage in the recent state, except at a little behind and below its centre, where is an ovoid depression (fovea capitis femoris), for the attachment for the Ligamentum teres.
 |
| Fig. 235. Right hip-joint, from behind. (The joint capsule, except for the strengthening ligaments, has been removed.) (Spalteholz.) |
Quote p. 263
Fibro-cartilage is found at the point of insertion of the ligamentum teres into the head of the femur, in the intervertebral disks, in the pubic symphysis, and in the interarticular cartilages.
 |
| Fig. 236. Right hip-joint from the medial side. (The bottom of the acetabulum has been chiselled away sufficiently to make the head of the femur visible.) (Spalteholz.) |
Quote pp. 306-307
Supplemental
Bands of the Capsular Ligament. In addition to the coraco-humeral ligament, the
capsular ligament is strengthened by supplemental bands in the interior of the
joint. One of these bands is situated on the inner side of the joint, and
passes from the inner edge of the glenoid cavity to the lower part of the lesser
tuberosity of the humerus. This is sometimes known as Flood's ligament, and is
supposed to correspond with the ligamentum teres of the hip-joint. A second of
these bands is situated at the lower part of the joint, and passes from the under
edge of the glenoid cavity to the under part of the neck of the humerus, and is
known as Schlemm's ligament. A third, called the gleno-humeral ligament, is situated
at the upper part of the joint, and projects into its interior, so that it can be
seen only when the capsule is opened. It is attached above to the apex of the glenoid
cavity, close to the root of the coracoid process, and, passing downward along
the inner edge of the tendon of the Biceps, is attached below to the lesser tuberosity
of the humerus, where it forms the inner boundary of the upper part of the
bicipital groove. It is a thin, ribbon-like band, occasionally quite free from the
capsule.
 |
| Fig. 237. The right hip-joint, seen from before. (Toldt.) |
Quote pp. 327-328
I. The Hip-joint (Articulatio Coxae) (Figs. 234, 235, 236, 237, 238, 239). This articulation is an enarthrodial or ball-and-socket joint, formed by the reception of the head of the femur into the cup-shaped cavity of the acetabulum. The articulating surfaces are covered with cartilage, that on the head of the femur being thicker at the centre than at the circumference, and covering the entire surface, with the exception of a depression just below its centre for the ligamentum teres; that covering the acetabulum is much thinner at the centre than at the circumference. It forms an incomplete cartilaginous ring of a horseshoe shape, being deficient below, where there is a circular depression, which is occupied in the recent state by a mass of fat covered by synovial membrane. The ligaments of the joints are the Capsular. Ilio-femoral. Transverse. Teres. Cotyloid.
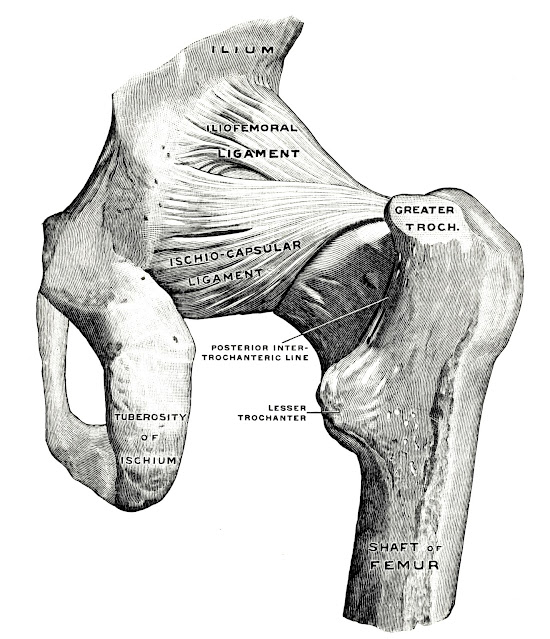
 |
| Fig. 238. Hip-joint, showing the ilio-femoral ligament. (After Bigelow.) |
Quote p. 331
The Ligamentum Teres, or the Interarticular Ligament (ligamentum teres femoris) (Figs. 236, 237, and 239) is a triangular band implanted by its apex into the depression a little behind and below the centre of the head of the femur, and by its broad base into the margins of the cotyloid notch, becoming blended with the transverse ligament. It is formed of connective tissue, surrounded by a tubular sheath of synovial membrane. Sometimes only the synovial fold exists. Very rarely it is absent. The ligament is made tense when the hip is semiflexed, and the limb adducted and rotated outward; it is, on the other hand, relaxed when the limb is abducted. It has, however, but little influence as a ligament, though it may to a certain extent limit movement, and would appear to be merely a "vestigial and practically useless ligament." 1 It is probably a modification of the folds which in other joints fringe the margins of reflection of synovial membranes.
 |
| Fig. 239. Right hip-joint. Frontal section. Posterior half, viewed from in front. (The joint surfaces have been somewhat pulled apart.) (Spalteholz.) |
Quote p. 331
Synovial Membrane (Figs. 237 and 239). The synovial membrane is very extensive. Commencing at the margin of the cartilaginous surface of the head of the femur, it covers all that portion of the neck which is contained within the joint; from the neck it is reflected on the internal surface of the capsular ligament, covers both surfaces of the cotyloid ligament and the mass of fat contained in the depression at the bottom of the acetabulum, and is prolonged in the form of a tubular sheath around the ligamentum teres, as far as the head of the femur. It sometimes communicates through a hole in the capsular ligament between the inner band of the Y-shaped ligament and the pubo-femoral ligament with a bursa situated on the under surface of the Ilio-psoas muscle.
 |
| Fig. 240. Relation of muscles to hip-joint. (Henle.) |
Quote pp. 334-335
The
hip-joint presents a very striking contrast to the shoulder-joint in the much
more complete mechanical arrangements for its security and for the limitation
of its movements. In the shoulder, as we have seen, the head of the humerus is
not adapted at all in size to the glenoid cavity, and is hardly restrained in
any of its ordinary movements by the capsular ligament. In the hip-joint, on
the contrary, the head of the femur is closely fitted to the acetabulum for a
distance extending over nearly half a sphere, and at the margin of the bony cup
it is still more closely embraced by the cotyloid ligament, so that the head of
the femur is held in its place by that ligament even when the fibres of the
capsule have been quite divided (Humphry). The anterior portion of the capsule,
described as the ilio-femoral ligament, is the strongest of all the ligaments
in the body, and is put on the stretch by any attempt to extend the femur
beyond a straight line with the trunk. That is to say, this ligament is the
chief agent in maintaining the erect position without muscular fatigue; for a
vertical line passing through the centre of gravity of the trunk falls behind
the centres of rotation in the hip-joints, and therefore the pelvis tends to
fall backward, but is prevented by the tension of the ilio-femoral and capsular
ligaments. The security of the joint may be also provided for by the two bones
being directly united through the ligamentum teres; but it is doubtful whether
this so-called ligament can have much influence upon the mechanism of the
joint. Flexion of the hip-joint is arrested by the soft parts of the thigh and
abdomen being brought into contact when the leg is flexed on the thigh; and by
the action of the hamstring muscles when the leg is extended; (1) extension, by
the tension of the ilio-femoral ligament and front of the capsule; adduction,
by the thighs coming into contact; adduction, with flexion by the outer band of
the ilio-femoral ligament, the outer part of the capsular ligament: abduction,
by the inner band of the ilio-femoral ligament and the pubo-femoral band;
rotation outward, by the outer band of the ilio-femoral ligament; and rotation
inward, by the ischio-capsular ligament and the hinder part of the capsule. The
muscles which flex the femur on the pelvis are the Psoas, Iliacus, Rectus,
Sartorius, Pectineus, Adductor longus and brevis, and the anterior fibres of
the Gluteus medius and minimus. Extension is mainly performed by the Gluteus
maximus, assisted by the hamstring muscles. The thigh is adducted by the
Adductor magnus, longus, and brevis, the Pectineus, the Gracilis, and lower part
of the Gluteus maxirnus, and abducted by the Gluteus medius and minimus and
upper part of the Gluteus maximus. The muscles which rotate the thigh inward
are the anterior fibres of the Gluteus medius, the Gluteus minimus, and the Tensor
fascia femoris; while those which rotate it outward are the posterior fibres of
the Gluteus medius, the Pyriformis, Obturator externus and internus, Gemellus superior
and inferior, Quadratus femoris, Iliacus, Gluteus maximus, the three Adductors,
the Pectineus, and the Sartorius.
1) The
hip-joint cannot be completely flexed, in most persons, without at the same
time flexing the knee, on account of the shortness of the hamstring muscles.
Cleland, Jour, of Anat. and Phys., No. 1, Old Series, p. 87.
External links
Gray H. Anatomy, descriptive and surgical; 17th ed. Philadelphia, New
York: Lea & Febiger, 1908. [hdl.handle.net]
Authors & Affiliations
Henry Gray (1825-1861) was a British anatomist and surgeon. [wikipedia.org]
 |
| Henry Gray Author: H. Pollock, unknown date; original in the wikimedia.org collection (CC BY 4.0, no changes). |
Keywords
ligamentum capitis femoris, ligamentum teres, ligament of head of femur, anatomy, functions
NB! Fair practice / use: copied for the purposes of criticism, review, comment, research and private study in accordance with Copyright Laws of the US: 17 U.S.C. §107; Copyright Law of the EU: Dir. 2001/29/EC, art.5/3a,d; Copyright Law of the RU: ГК РФ ст.1274/1.1-2,7


Comments
Post a Comment