TIKTAALIK ROSEAE
The first truly
tetrapod animal (Limbed tetrapods) is recognized as the lobe-finned fish
Tiktaalik roseae (clade Elpistostegalia), discovered in rocks aged about 375 Ma (2006DaeschlerEB_JenkinsJrFA; 2008ShubinN; 2017ShubinN).
Discoveries in recent years have allowed us to place the taxa of early
tetrapodomorphs in the following order: Tinirau, Eusthenopteron, Megalichthys,
Panderichthys, Qikiqtania, Tiktaalik, Elpistostege, Parmastega, Ventastega,
Acanthostega, Elginerpeton, Ymeria, Ichthyostega (2022StewartTA_ShubinNH). The
closest ancestor of Tiktaalik roseae, the fragments of the skeleton of which
are relatively well preserved, is Panderichthys.
 |
| Reconstruction of the prehistoric fish Pandericthys Author Tyler Rhodes; original in the wikipedia.org collection (license CC BY-SA 3.0, no changes). |
The shape of the skeleton of the pectoral fin and shoulder girdle suggests that Panderichthys rhombolepis "walked" (2006AhlbergPE_ClackJA). At the very least, the animal could crawl from shallow waters in search of prey by bending its body, fixing its position alternately with the pectoral and pelvic fins (1992VorobyevaEI_KuznetzovA).
The appearance of
Tiktaalik roseae differs only slightly from the above-mentioned creature.
 |
| 3-D model of Tiktaalik roseae (clade Elpistostegalia); original image on sketchfab.com. |
The pelvic bones of Tiktaalik roseae are paired, have wide iliac processes, flat and elongated pubic bones, and acetabulums – deep sockets bordered by a strong lip. The pelvis is enlarged compared to other fin tetrapodomorphs. Despite its size and strength, it retains primitive features: the absence of an ischium and attachment of the sacral rib. The acetabulum of Tiktaalik roseae is a pit with a smooth surface. It is relatively round in shape and much deeper than the corresponding articular surface in Gooloogongia or Eusthenopteron. The acetabulum of Tiktaalik roseae is located in the caudal part of the pelvis. As in other fin tetrapodomorphs, it is directed more laterally than in fishes, but less than in tetrapods. Tiktaalik roseae is a mosaic of primitive and derived states: like fishes, its acetabulum is located on the caudal edge of the pelvis, but is more similar to that of tetrapods in that it faces outward (2014ShubinNH_JenkinsFA). The pelvic bones of Tiktaalik roseae are thought to have been connected into a single structure by a cartilaginous element located between the opposite pubic processes, as in Eusthenopteron foordi (1970AndrewsSM_WestollTS).
The
acetabulum of early tetrapodomorphs had an elongated shape, in particular, the
ratio of its length to height was 0.60 in Medoevia, 0.60 in Eusthenopteron,
0.42 in Tinirau, 0.48 in Panderichthys, and 0.44 in Tiktaalik (2012SwartzB).
Accordingly, the hip joint of the ancestral forms of tetrapods was ellipsoid,
similar to the joints of humans lacking internal ligaments: wrist,
metacarpophalangeal, calcaneocuboid, and sternoclavicular. It is unlikely that
the biaxial hip joint of tetrapodomorphs had a ligamentum capitis femoris (LCF)
inside, but possibly on the periphery.
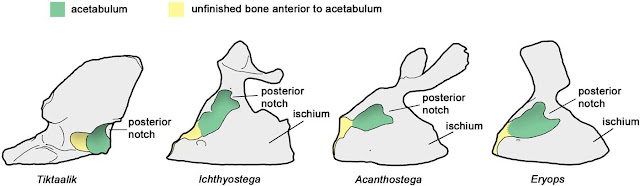
P.E. Ahlberg (2018)
first draws attention to the presence of a posterior acetabular notch in
Tiktaalik roseae.
After examining the 3D model of the pelvic bone of Tiktaalik roseae, we noticed a second notch in the anterior part (Tweet of Nov 23, 2020).
 |
| 3-D model of the pelvis of Tiktaalik roseae; the anterior and posterior notches of the acetabulum are indicated by arrows; original: media.hhmi.org. |
It seems that
paired LCFs typical of modern salamanders were attached to them
(1934FrancisETB).
 |
| Hip joint of the Japanese salamander, arrows indicate two LCF analogues; image of a part of the exhibit of the Zoological Museum of Moscow State University (photo by the author). |
The anterior and
posterior LCFs (posterior and anterior) were attached to diametrically opposite
notches of the acetabulum of Tiktaalik roseae. In accordance with the
subdivision of the pelvic bone, their synonyms are acceptable: ilium and pubic
LCF. Probably, within the above-mentioned notches not only LCF were attached,
but also their proximal ends moved. LCF functioned during movements in shallow
water and out of water. In our opinion, locomotion was carried out by bending
the body and alternately turning the pelvic girdle in tacks in the direction of
the general ray of movement. The femurs were installed diagonally. One of them
was directed with its distal end laterally and cranially, and the opposite one
was directed laterally and caudally. The rotation of the body in the horizontal
plane dragged the pelvis along with it. In this case, it received support from
two LCFs at once. The LCF posterior was stretched in the hip located in front,
and the LCF anterior in the contralateral hip located behind. These structures
"worked" as flexible supporting elements - stretchers, holding the
levers of the femurs in extreme positions of supination and pronation.
 |
| 3-D model of the right pelvic bone of Tiktaalik roseae, view from the outside-back-bottom; We have depicted the proximal parts of two LCFs (posterior et anterior) attached to the anterior and posterior notches of the acetabulum, below is our reconstruction of the femur with LCF fragments; original pelvis model: media.hhmi.org. |
References
Daeschler EB, Shubin NH, Jenkins Jr FA. A Devonian tetrapod-like fish and the evolution of the tetrapod body plan. Nature. 2006;440(7085)757-63. [stuartsumida.com]
Shubin N. Your inner fish: a journey into the 3.5-billion-year history of the human body. New York: Vintage books, 2008. [books.google , bookreadfree.com]
Шубин Н. Внутренняя рыба. История человеческого тела с древнейших времен до наших дней. Пер с англ. П. Петрова. Москва: Издательство АСТ, CORPUS, 2017. [img-gorod.ru]
Stewart TA, Lemberg JB, Daly A, Daeschler EB, Shubin NH. A new elpistostegalian from the Late Devonian of the Canadian Arctic. Nature. 2022;608(7923)563-8. [nature.com]
Ahlberg PE, Clack JA. Palaeontology: a firm step from water to land. Nature 2006;440(7085)747-9. [nature.com , cloudfront.net]
Vorobyeva EI, Kuznetzov A. In Fossil Fishes as Living Animals. In: Mark-Kurik E (Ed). Fossil fishes as living animals. Tallinn: Academy of Sciences of Estonia, 1992:131-140. [kirjandus.geoloogia.info]
Shubin NH, Daeschler EB, Jenkins FA. Pelvic girdle and fin of Tiktaalik roseae. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 2014;111(3)893-9. [pnas.org]
Andrews SM, Westoll TS. IX - The postcranial skeleton of Eusthenopteron foordi Whiteaves. Transactions of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. 1970;68(9)207-329. [cambridge.org]
Swartz B. A marine stem-tetrapod from the Devonian of Western North America. PLOS ONE. 2012;7(3)e33683. [ncbi.nlm.nih.gov]
Ahlberg PE. Follow the footprints and mind the gaps: a new look at the origin of tetrapods. Earth and Environmental Science Transactions of the Royal Society of Edinburgh. 2018;109(1-2)115-37. [cambridge.org]
Francis ETB. The anatomy of the salamander. Oxford: The Clarendon Press, 1934. [archive.org]
Keywords
ligamentum capitis femoris, ligamentum teres, ligament of head of femur, doctrine, animals, fish
The original text in Russian is available at the link: Tiktaalik roseae
NB! Fair practice / use: copied for the purposes of criticism, review, comment, research and private study in accordance with Copyright Laws of the US: 17 U.S.C. §107; Copyright Law of the EU: Dir. 2001/29/EC, art.5/3a,d; Copyright Law of the RU: ГК РФ ст.1274/1.1-2,7


Comments
Post a Comment