Publications about the LCF in July 2024
Salas, A. P., Lara-Albisua, J. L. P., Taffinder-Villarreal, D. S., & Mazek, J. (2024). Postless Hip Arthroscopy for Labrum Reconstruction and Labrum Augmentation. Arthroscopy Techniques, 103092. [i] arthroscopytechniques.org , sciencedirect.com
Mat, C. M. H. B. C., Sulaiman, A. R., & Noor, N. M. (2024). Early Versus Late Fixation of Paediatric Femoral Neck Fractures: A systematic review and meta-analysis. [ii] opendata.usm.my
Mishima, K., Kamiya, Y., Sawamura, K., Matsushita, M., & Imagama, S. (2024). Gradual Reduction Using Overhead Traction for Late-Detected Developmental Dysplasia of the Hip: A Report of Three Cases Diagnosed Among Children Over Four Years Old. Cureus, 16(7). [iii] assets.cureus.com
Siebenrock, K. A., Steppacher, S. D., Ziebarth, K., Schwab, J. M., & Büchler, L. (2024). Modified Dunn Procedure for Open Reduction of Chronic Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis. JBJS essential surgical techniques, 14(3), e23. [iv] journals.lww.com
Ilaka, O., Patel, S., Lemos, N., Argoff, C., Martin, H. D., & De, E. (2024). Neurologic pelvic pain: Diagnosis and treatment, with attention to hip-spine-pelvis exam. Continence, 101329. [v] sciencedirect.com
Alberto, L. R., Jesús, P. O., Marco, S. O., & Juan, R. Z. (2024). Ten years of Minimum Follow-Up After Hip Arthroscopy. Personal Series and Results. Acta Scientific Orthopaedics (ISSN: 2581-8635), 7(7). [vi] researchgate.net
Стрижков, А. Е., Нуриманов, Р. З., & Николенко, В. Н. (2022). Критические периоды внутриутробного морфогенеза связочного аппарата тазобедренного сустава. Медицинский вестник Северного Кавказа, 17(4), 417-421. [vii] medvestnik.stgmu.ru
Pré, C. A. G. (2024). The Hepatic Piston Mechanism in Crocodylomorpha: Functional Anatomical Reconstructions in Terrestrial and Aquatic Taxa. (Doctoral dissertation, Louisiana State University Health Sciences Center). [viii] proquest.com
Hartmann, K. T., Odgaard, A., Knudsen, U. K., Aalbaek, B., Kvich, L., Birch, J. M., ... & Jensen, L. K. (2024). First Hip Hemiarthroplasty in Göttingen Minipigs; Surgical and Post-mortem Protocol. Research Square. [ix] researchsquare.com
Hatem, M., Badejo, M., McCarroll, M., Feng, R., & Martin, H. D. (2024). The predominant insertion of the ischiofemoral ligament is a merging to the iliofemoral ligament as demonstrated on magnetic resonance arthrogram studies. Acta Radiologica, 02841851241263584. [x] journals.sagepub.com
Tachibana, T., Katagiri, H., Matsuda, J., Ozeki, N., Watanabe, T., Sekiya, I., & Jinno, T. (2024). Biomechanical analysis of load distribution in porcine hip joints at different acetabular coverages. BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders, 25(1), 576. [xi] link.springer.com
Zecca, F., Shah, A., Guggenberger, R., Iyengar, K.P., Botchu, R., Shah, A. (2024). Bone Trauma. In: Medical Radiology (1-74). Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. [xii] link.springer.com
Ketema, A. A., Gebregiorigis, B. T., Abera, M. T., Amha, L. G., & Semayneh, S. W. (2024). Post radiotherapy femoral head avascular necrosis. Radiology Case Reports, 19(10), 4289-4292. [xiii] sciencedirect.com
Liang, D., Pei, J., Zhang, X., Pei, R., & Chen, X. (2024). Surgical hip dislocation technique through the femoral head fovea fenestration and impaction bone grafting for the treatment of non-traumatic osteonecrosis of the femoral head: a retrospective study. Journal of Orthopaedic Surgery and Research, 19. 437. [xiv] josr-online.biomedcentral.com
NB! Fair practice / use: copied for the purposes of criticism, review, comment, research and private study in accordance with Copyright Laws of the US: 17 U.S.C. §107; Copyright Law of the EU: Dir. 2001/29/EC, art.5/3a,d; Copyright Law of the RU: ГК РФ ст.1274/1.1-2,7
[i] If the ligamentum teres is torn, we perform ligamentum teres debridement or reconstruction in a standard fashion.
[ii] In children under four years, the femoral head relies on the metaphyseal vessel penetrating the growth plate, the lateral epiphyseal vessel in the retinacula, and the limited vessel in the ligamentum teres. After age four, the metaphyseal vessels diminish, and by ages four to seven, the femoral head depends almost entirely on the lateral epiphyseal vessels.
[iii] Considering possible precautions against AVN [avascular necrosis], such as prior adductor tenotomy, the addition of Bryant’s vertical traction in the second step before abducting the hips [15], a gradual increase in knee flexion during the third step, and a slower incremental decrease in weight after reduction, may be necessary, especially for children aged five years, to suppress an impact of reduction on pathological intracapsular structures, including the hypertrophic pulvinar, ligamentum teres, and limbus, and a sustained inflammatory reaction induced inside and outside the reduced hip.
[iv] The femoral epiphysis is pinned in situ (in unstable cases) with threaded Kirschner wires, the ligamentum teres is transected, and the femoral head is dislocated.
[v] (2) Capsule/ labral: The labrum and hip capsular
ligaments are designed to offload some force created by the proximal femur in
the acetabulum. The iliofemoral, pubofemoral, ischiofemoral ligaments along
with the ligament of teres comprise the capsular ligaments, which function to
stabilize the hip during extension/ flexion [8].
8. Martin,
H. D. Palmer I.J., Hatem, M. (2022).
Physical examination of the hip and pelvis. In Hatem, M., Khoury, A. N., &
Martin, H. D. (Eds). Hip Arthroscopy and Hip Joint Preservation Surgery (pp. 139-159). Cham: Springer International Publishing.
[link.springer.com]
…
(3) Supine Position for the HSP [hip spine pelvis] examination: (1) Flexion adduction internal rotation test and (2) Flexion abduction external rotation test. Flexion, adduction, and internal rotation of the leg in the supine position causing hip pain can indicate a premature osseous abutment or CAM deformity. FABERS (flexion, abduction, and external rotation) can be used to screen the ligament of teres function, femoral anteversion or some pubofemoral ligament contribution or SI complaints. In general, recreation of pelvic complaint with end range of motion for the hip indicates the possibility of hip contribution to the pelvic complaint.
[vi] A total of 11 psoas tenotomies were performed (19.29% of cases). Only 1 patient had a round ligament injury, which was treated by vaporizer remodeling.
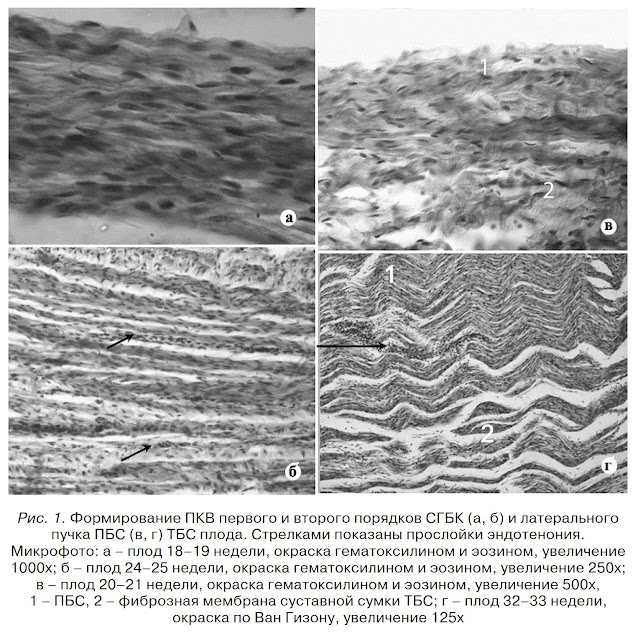
[vii] Результаты и обсуждение. Закладка связок ТБС
происходит неравномерно. Раньше всех на 12 неделе внутриутробного развития
макроскопически выявляется связка головки бедренной кости (СГБК). Форма связки
у места начала уплощенная, в средней части – эллипсовидная, у места
прикрепления на 12–15 неделях внутриутробного развития – плоская. Однако на
20–21 неделях она приобретает округлую форму, сохраняющуюся до рождения. На
протяжении плодного периода связка растет относительно равномерно (табл.).
…
Гистологическое строение
СГБК в плодном периоде отличается от внесуставных связок ТБС. На 14–15 неделе
внутренняя структура СГБК определялась скоплением вытянутых клеток
фибробластического ряда с овальными ядрами, ориентированных вдоль оси связки.
На 18–19 неделях в межклеточном пространстве связки определяются ПКВ,
организующиеся в пучки первого порядка. На 20–21 неделях ПКВ первого порядка –
основа фиброструктуры СГБК на всем ее протяжении. На 24–25 неделях между
отдельными ПКВ первого порядка обнаруживаются тонкие прослойки эндотенония
(рис. 1). На 28–29 неделях эти участки рыхлой соединительной ткани достигают
максимальной ширины и разделяют ПКВ второго порядка.
…
Предельная относительная
деформация (удлинение) наибольшие значения показала у внесуставных связок на
20–21 и 28–31 неделях. У СГБК показатель на протяжении плодного периода
постоянно увеличивался (рис. 2). Однако с 28 по 33 неделю изменения показателя
не были статистически значимы.
…
Выделены два критических
периода (18–21 и 28–31 неделя), характеризующиеся задержкой роста, изменением
структуры и экстремумом биомеханических свойств связок, которые определяются
изменениями динамического стереотипа проксимального сегмента скелета
конечностей плода.
[viii] This additional cartilaginous surface, along with the intraacetabular femoral ligament, the ligamentum capitis femoris, both protect and allow the mobility necessary (in the form of femoral dislocation from the acetabulum) for crocodylians…
[ix] Caput femoris was
elevated from the acetabular cup by a Hohmann retractor, and the femoral head
ligament was cut by curved scissors.
…
Before the
reduction of the joint, the acetabular cup was cleared up for remnants of the
femoral head ligament.
…
The present
study identified several points of awareness when performing a hip
hemiarthroplasty in minipigs. First, there is a risk of caudodorsal dislocation
despite postoperative confirmation of the suitability of the acetabular cup's
conformation around the hip hemiarthroplasty. This may be due to the flat
acetabular cup anatomy of Göttingen minipigs, which does not naturally encircle
the entire femoral head, relying on stability from the femoral head ligament
(Fig. 7).
…
The following points are important to prevent dislocation: 1) If the prosthesis's angulation is excessively retrograde (retroversion), the risk of the prosthetic head slipping over the caudal acetabular brim is increased. 2) Cleaning the acetabular cup with complete removal of the femoral head ligament is crucial to secure adequate space in the acetabular cup and ensure optimal head-to-acetabulum contact.
[x] The ISFL is known to be the main ligamentous restrictor of hip internal rotation, while the ILFL is the main restrictor of hip external rotation. ... ligaments at the hip joint work in synchrony with the acetabulum and femoral head for articular stability.
[xi] With the
femur fixed in the proper orientation, the pelvis was secured with polymethyl
methacrylate and was secured to the testing machine. The hip capsule and the
wires securing the orientation of the hip joint were removed after setting. The
labrum and ligamentum teres were preserved (Fig. 1-C).
…
The sensor was selected and placed to maximize the contact area in the hip joint and minimize wrinkling. The inner edge of the sensor placement was positioned just outside the attachment of the ligamentum teres, and the anterior edge of the sensor was aligned with the anterior edge of the contact area in the neutral position.
[xii] Four major ligaments, one intracapsular and three extracapsular, contribute to stabilizing the hip joint.
…
The ligamentum teres runs from the cotyloid fossa to the fovea femoris and hosts a small arterial branch for the femoral head provided by the obturator artery..
[xiii] Other contributing factors in cancer patients include metastatic infiltration, hypercoagulability, and the congenital absence of the ligamentum teres artery [1]. 1. Daoud, A. M., Hudson, M., Magnus, K. G., Huang, F., Danielson, B. L., Venner, P., ... & Fairchild, A. (2016). Avascular necrosis of the femoral head after palliative radiotherapy in metastatic prostate cancer: absence of a dose threshold?. Cureus, 8(3). [assets.cureus.com]
[xiv] Use a retractor to retract and protect the osteotomy fragment, expose the joint capsule, perform a “Z” incision on the joint capsule, retract and flex the hip joint, and then sever the round ligament to complete the femoral head dislocation.



Comments
Post a Comment