Traumatic Open
Anterior Hip Dislocation in an Adult Male: A Case Report
Anderson Freitas, Vincenzo Giordano Neto, Patrick F. Godinho, Silvio L. Macedo, Vinicius F. Ribeiro de Oliveira, Gary Alan A. Montano, Celio Silva, Vanessa C. Bandeira
Abstract
This case report describes the surgical treatment and one-year follow-up of an adult male patient, who was treated for a severe anterior open hip dislocation fracture with no sign of femoral head necrosis and maintaining a Harris Hip Score (HHS) of 93.
Introduction
The hip is a joint that has great stability, intrinsically due to its ball-and-socket shape and extrinsically due to its ligaments and strong muscles. A high-energy trauma is needed to cause the dislocation of the hip. Anterior hip dislocations are very uncommon and constitute 10%-15% of the traumatic displacements of this joint. However, when they do occur, they could be associated with brain, thoracic, and abdominal lesions as well as local lesions, such as neurological or severe vascular injuries, requiring immediate intervention. A reserved prognosis, due to the high rate of complications such as deep infections, femoral head necrosis, severe functional limitation, and arthrosis, is observed in several published case reports [1- 5]. The authors describe the follow-up of a fracture and a severe anterior dislocation of the hip in a young adult who surprisingly had a good outcome in the one-year follow-up, with a Harris Hip Score (HHS) of 93, no necrosis of the femoral head, and with only a slight degree of arthrosis.
Case
Presentation
We present the case of a 28-year-old male who suffered a high-energy motorcycle accident. At admission, the patient was conscious, Glasgow coma scale (GCS) 15, hemodynamically stable, and presenting superficial excoriations on the trunk and lower limbs. However, there was a wound of approximately 20 cm on the lateral aspect of the right hip at the level of the greater trochanter, exposing the entire proximal end of the femur (Figure 1).
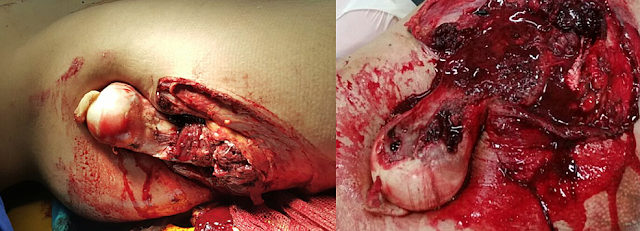 |
| Figure 1: A photograph of the lesion in the right hip region, showing the exposure of the entire proximal end of the femur |
After a clinical evaluation and imaging tests that excluded cranial or abdominal disorders, we prioritized the neurovascular examination of the affected limb, which did not present complications, and the protection of the femoral head with the use of moistened gauze and saline solution. Radiographs in the anteroposterior view of the right hip showed a hip dislocation with a greater trochanter fracture (Figure 2).
 |
| Figure 2: A radiograph of the right hip showing the dislocation with a fracture of the greater trochanter |
An exhaustive irrigation of the acetabular cavity and the exposed femur was performed, using 10 liters of saline solution at 9% when the patient was in the surgical room. The procedure happened under sedation and spinal anesthesia. A large debridement of muscle, fascia, and bone tissues was required to remove all the devitalized tissue, considered viable only when active bleeding and the clean appearance of the open wound was observed through direct vision by the surgeons.
The fractured fragment of the greater trochanter was fixed with two 6.5 mm cancellous screws and washers at the proximal end of the femur (Figure 3).
 |
| Figure 3: Image of a radiograph after surgery, showing hip reduction and the fixation of the greater trochanter |
After a revision of the debridement sites and radioscopic control of the
hip reduction and fixation, the wound was closed (Figure 4).
 |
| Figure 4: Picture of the lesion, showing the closure of the wound after surgery |
After the first 48 hours of surgery, the wound was releasing a significant amount of secretion, bloody and serum like, and a strong odor was observed, with no laboratory exams indicating infection. At this time, a new surgical procedure (second look) with greater aggressiveness was obtained, removing all devitalized tissue and bad-in-appearance cutaneous cover, which was not necrotic but had an unhealthy appearance (Figure 5).
 |
| Figure 5: Picture of the wound after second-look surgery |
A vacuum-assisted closure was used (Figure 6).
 |
| Figure 6: Picture of the vacuum-assisted closure of the wound |
The
vacuum-assisted closure was changed every week for four weeks until the
appearance of granulation tissue at the surface of the surgical wound (Figure
7). During this period, the patient's laboratory exams showed a drop in the
hemoglobin level, resulting in a 7.1 g/dl result, which was corrected with
a transfusion of 600 ml of red blood cell (RBC) concentrate. As a
rehabilitation procedure, we started daily physiotherapy with passive limb
mobility and activity, within pain limits, with no load on the right hip.
 |
| Figure 7: Picture of the wound after four weeks of vacuum-assisted closure |
In the
fifth week, a new surgical procedure was performed for skin grafting. It was
performed with no major occurrences and implantation of the graft was
successful. Shortly after the removal of the stitches from the graft surgery,
in about eight weeks, partial weight bearing on the affected limb was initiated
with the use of two crutches.
After a one-year follow-up, the patient had good mobility of the affected limb (Figure 8) without significant pain during mobilization and examination of the joint, with a Harris Hip Score of 93 points.
 |
| Figure 8: Pictures of the patient at the one-year follow-up |
The radiograph showed a decrease of the articular space in the right hip (Figure 9) but the magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) showed no necrosis of the femoral head. (Figure 10). He was able to ride a bicycle, run, and do squats.
 |
| Figure 9: Radiograph showing the healing of the greater trochanter fracture and a narrowing of the hip joint space |
 |
| Figure 10: Pictures of the MRI, showing the reduction of the articular space and no necrosis of the femoral head |
Discussion
An open
anterior dislocation of the hip is a severe trauma with only a few reports
described in the literature. Therefore, due to the rarity of the cases, especially
in adult patients, there is a lack of treatment guidelines [1].
An early
diagnosis with image evaluation is very important for initial treatment and
follow-up [2].
Immediate
care with precautions taken during the reduction and subsequent debridement
procedures, followed by the use of vacuum-assisted wound closure, may be a
determinant of good outcomes by avoiding the occurrence of a deep infection [3].
Load
restriction and early rehabilitation may have been a differential to avoid the
complications of femoral head cartilage lesions, as greater pain limits the
range of movement [4-5].
As seen
earlier in literature, the fracture of the greater trochanter could be a
protective factor for femoral head vascularization, especially if the fragment
suffers a posterior deviation, sometimes being able to preserve the insertion
of the external rotators. This may have been a reason for the maintenance of
the medial circumflex artery close to the greater trochanter, allowing vascular
restoration on the femoral head after reduction and fixation [6].
There is still no protocol or guideline for this type of fracture. Therefore, it is very clear that taking precautions during procedures such as reduction, cleaning, fixation, and rehabilitation is very important to achieve a better result and avoid or postpone the complications of this very serious fracture.
Conclusions
The very low number of cases like this in the literature leads us to affirm that there is no specific protocol to be followed. A functional limitation of the hip was imposed according to what was described previously in the literature. However, the absence of osteonecrosis, until this moment, showed a different result from all the case reports analyzed by the authors. The maintenance of vascularization from the femoral head made us believe that the association of a greater trochanter fracture with this pathology may be the reason for this outcome.
References
1. Tornetta
P 3rd: Hip Dislocations and Fractures of the Femoral Head. Michael S.H. Kain
(ed): Williams and Wilkins, 2006. 1716-1752.
2. Erb RE,
Steele JR, Nance Jr EP, et al.: Anterior dislocation of the hip: spectrum of
plain film and CT findings. Roentgenol. 1995, 165:1215-1219. 10.2214/ajr.165.5.7572506
3. Anderson
Luiz de Oliveira AL, Machado EG: Open anterior dislocation of the hip in an
adult: a case report and review of literature [Article in English, Portuguese].
Rev Bras Ortop. 2014, 49:94-97. 10.1016/j.rbo.2013.04.010
4. Şahin V,
Karakaş ES, Aksu S, Atlihan D, Turk CY, Halici M: Traumatic dislocation and
fracture-dislocation of the hip: a long-term follow-up study. J Trauma Acute
Care Surg. 2003, 54:520-529. 10.1097/01.TA.0000020394.32496.52
5. Mehlman
CT, Hubbard G, Crawford AH, Dennis RR, Wall EJ: Traumatic hip dislocation in children:
long-term followup of 42 patients. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2000, 376:68-79.
6. Freitas A, Macedo Neto SL: Apophysary fracture or avulsion of the greater trochanter. Acta Ortop Bras [online]. 2016, 24:164-166. 10.1590/1413-785220162403155803
External links
Freitas A, Neto VG, Godinho PF, Macedo SL, Ribeiro de Oliveira VF, Montano GAA, Silva C, Bandeira VC. Traumatic Open Anterior Hip Dislocation in an Adult Male: A Case Report. Cureus. 2018;10(6)e2862. doi:10.7759/cureus.2862 [cureus.com , cureus.com(PDF)]
Authors & Affiliations
Anderson Freitas (1), Vincenzo Giordano Neto (2), Patrick F. Godinho (3), Silvio L. Macedo (4), Vinicius F. Ribeiro de Oliveira (1), Gary Alan A. Montano (1), Celio Silva (1), Vanessa C. Bandeira (1)
1.
Instituto De Pesquisa E Ensino-Ipe, Hospital Ortopedico E Medicina
Especializada - Home, Brasilia, BRA
2. Orthopedics,
Hospital Municipal Miguel Couto, RIo De Janeiro, BRA
3.
Instituto De Pesquisa E Ensino-Ipe, Hospital Ortopedico E Medicina
Especializada-Home, Brasilia, BRA
4. Instituto De Pesquisa E Ensino-Ipe, Hospital Ortopedico E Medicina Especializada - Home, Braslia, BRA
Corresponding
author
Anderson Freitas, silviomneto31@gmail.com
Copyright
Freitas et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License CC-BY 3.0., which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
License
This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Keywords
ligamentum capitis femoris, ligamentum teres, ligament of head of femur, hip dislocation, open dislocation of hip, trauma, visualization, observation
. .
NB! Fair practice / use: copied for the purposes of criticism, review, comment, research and private study in accordance with Copyright Laws of the US: 17 U.S.C. §107; Copyright Law of the EU: Dir. 2001/29/EC, art.5/3a,d; Copyright Law of the RU: ГК РФ ст.1274/1.1-2,7
EXPERIMENTS AND OBSERVATIONS

Comments
Post a Comment